Can ChatGPT Truly Understand What We’re Saying? A Powerful Comparison with BERT” – Day 69
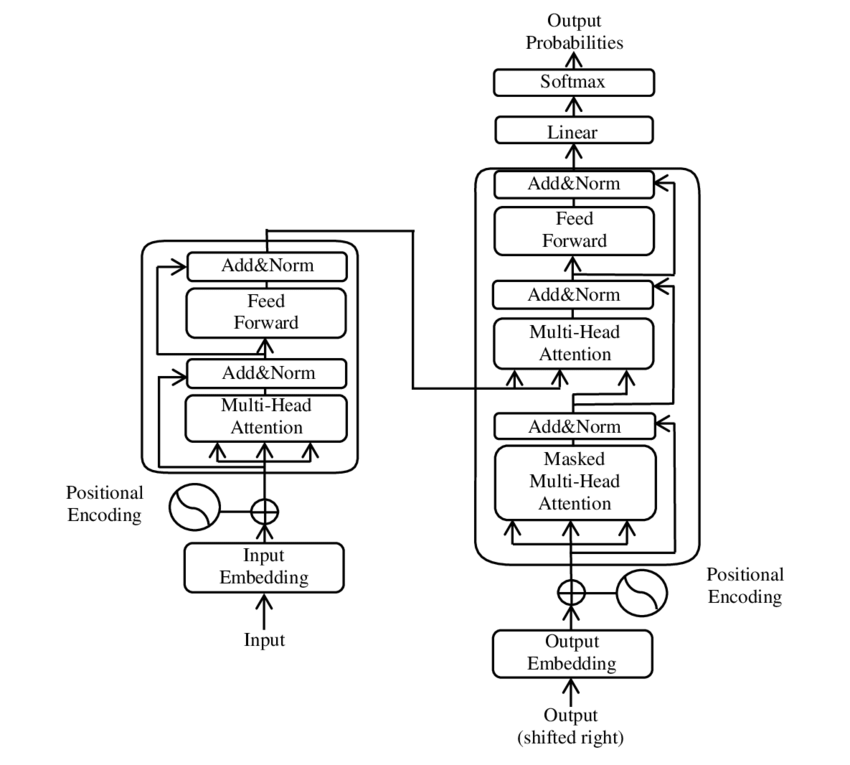
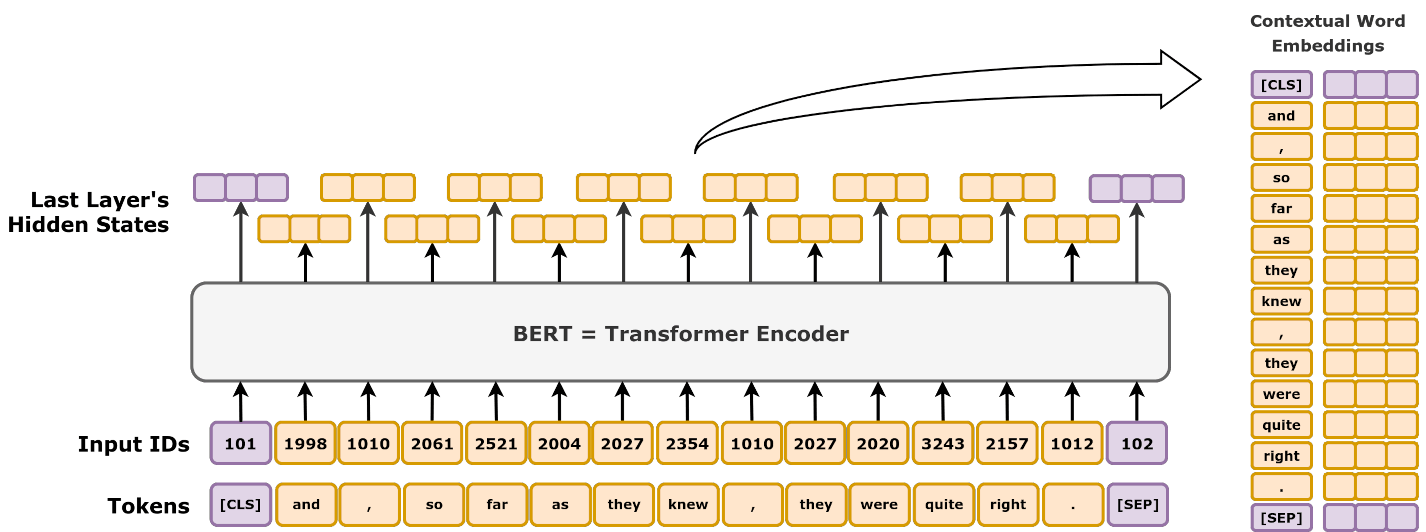
Transformer Models Comparison Feature BERT GPT BART DeepSeek Full Transformer Uses Encoder? ✅ Yes ❌ No ✅ Yes ❌ No ✅ Yes Uses Decoder? ❌ No ✅ Yes ✅ Yes ✅ Yes ✅ Yes Training Objective Masked Language Modeling (MLM) Autoregressive (Predict Next Word) Denoising Autoencoding Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) with Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) Bidirectional? ✅ Yes ❌ No ✅ Yes (Encoder) ❌ No Can be both Application NLP tasks (classification, Q&A, search) Text generation (chatbots, summarization) Text generation and comprehension (summarization, translation) Advanced reasoning tasks (mathematics, coding) Machine translation, speech-to-text Understanding ChatGPT and BERT: A Comprehensive Analysis by...