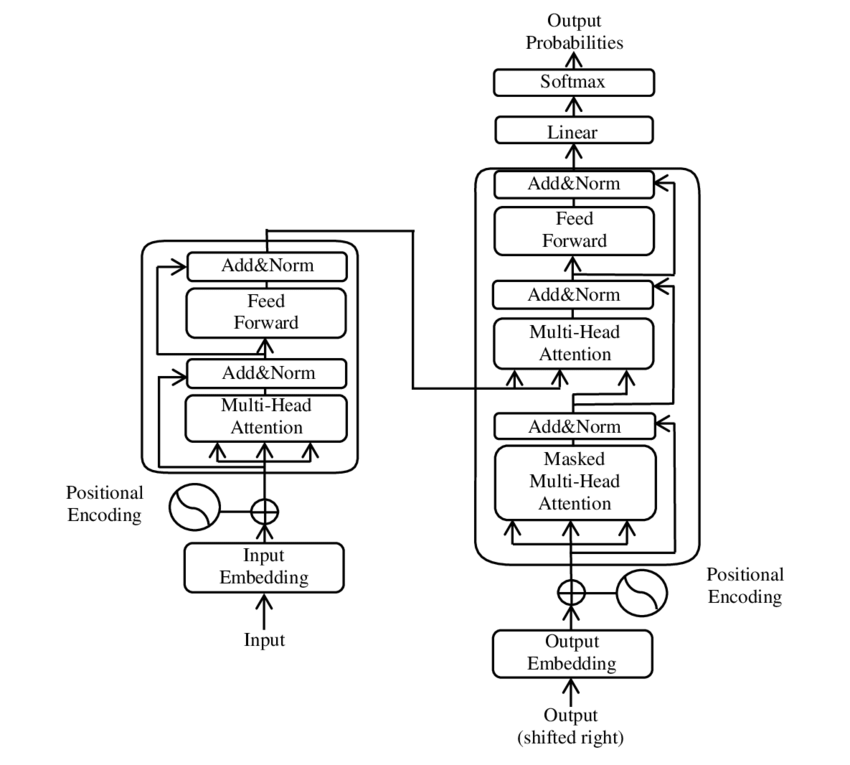
Understanding How ChatGPT Works: A Step-by-Step Guide ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is a sophisticated language model capable of generating human-like responses to various queries. Understanding its architecture and functionality provides insight into how it processes and generates text. 1. Input Processing: Tokenization and Embedding When ChatGPT receives a sentence, it first performs tokenization, breaking the input into individual units called tokens. These tokens can be words or subwords. Each token is then converted into a numerical vector through a process called embedding, which captures semantic information in a high-dimensional space. Example: For the input: “Write a strategy for treating otitis in a young adult,” the tokenization might yield tokens like “Write,” “a,” “strategy,” etc. Each of these tokens is then mapped to a corresponding vector in the embedding space. 2. Decoder-Only Architecture: Contextual Understanding and Response Generation Unlike traditional transformer models that utilize an encoder-decoder architecture, ChatGPT employs a decoder-only structure. This design allows the model to handle both understanding the input and generating responses within a single framework. The model uses self-attention mechanisms to capture relationships between tokens, enabling it to understand context and generate coherent outputs. Key Points: Self-Attention: Allows the model to weigh the importance of different tokens in the input sequence, facilitating a nuanced understanding of context. Autoregressive Generation: The model generates text one token at a time, using previously generated tokens to inform subsequent ones. 3. Attention Mechanism: Focusing on Relevant Information Within the decoder, the attention mechanism enables ChatGPT to focus on pertinent parts of the input when generating responses. For instance, when formulating a treatment strategy for “otitis,” the model emphasizes tokens related to medical treatment and conditions. Attention Mechanism Table: Token Attention Weight otitis 0.9 treating 0.8 young 0.2 adult 0.1 4. Output Generation:Producing the Final Response After processing the input and applying attention mechanisms, ChatGPT generates a response by predicting the next token in the sequence until it completes a coherent answer. This process involves selecting tokens with the highest probability at each step, ensuring the response is contextually appropriate and fluent. Transformer VS RNN To understand how ChatGPT works, we need to take a deeper look at how it updates its parameters during the learning process and how this is different from traditional RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks) and simpler neural networks. 1. Traditional Neural Networks & RNNs: Weight Updates In traditional neural networks, and even in RNNs, the core of the learning process lies in weight updates. Here’s how it generally works: Forward Pass: Data (e.g., text, images) is passed through layers of the neural network, where each neuron in a layer takes input from the previous layer and multiplies it by a weight. The weighted sum is passed through an activation function to introduce non-linearity (e.g., a ReLU or sigmoid function). Backward Pass (Backpropagation): After the network predicts an output, an error is calculated by comparing the predicted output to the actual output. The network then adjusts its weights in reverse order (from output to input), using backpropagation to minimize the error. The weight adjustments are based on gradients computed from the error using gradient descent. RNNs: In RNNs, the network processes sequences by maintaining hidden states across time steps. This allows it to “remember” previous inputs. However, RNNs struggle with long-term dependencies due to issues like vanishing gradients, which occur during backpropagation through many layers (or time steps). This is where transformers like GPT shine, as they don’t rely on this sequential processing. Key Differences Between RNNs and Transformers (ChatGPT) FeatureRNNsTransformers (ChatGPT)How Sequences are ProcessedSequentially (step by step)All at once (parallel processing)Handling Long-Range…
Brief OverView of How ChatGPT Works? – Day 68